Output : Différence entre versions
De Wiki
| Ligne 89 : | Ligne 89 : | ||
| Relative velocity in rotating frame | | Relative velocity in rotating frame | ||
| style=text-align:center; | m/s | | style=text-align:center; | m/s | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | A | ||
| + | | Semi-major axis | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | km | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | E | ||
| + | | Eccentricity | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | I | ||
| + | | Inclination | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AOP | ||
| + | | Aargument of perigee | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RAAN | ||
| + | | Right ascension of the ascending node | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | TA | ||
| + | | True anomaly | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MA | ||
| + | | Mean anomaly | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EA | ||
| + | | Eccentric anomaly | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | deg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EX | ||
| + | | First component of the eccentricity vector | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EY | ||
| + | | Second component of the eccentricity vector | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | HX | ||
| + | | First component of the inclination vector | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | HY | ||
| + | | Second component of the inclination vector | ||
| + | | style=text-align:center; | - | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Version du 11 juillet 2017 à 08:10
This tab allows to the user to specify how output data will be stored with the frequency, the inertial frame used for output data (could be different of the propagation frame) as well as local frame.
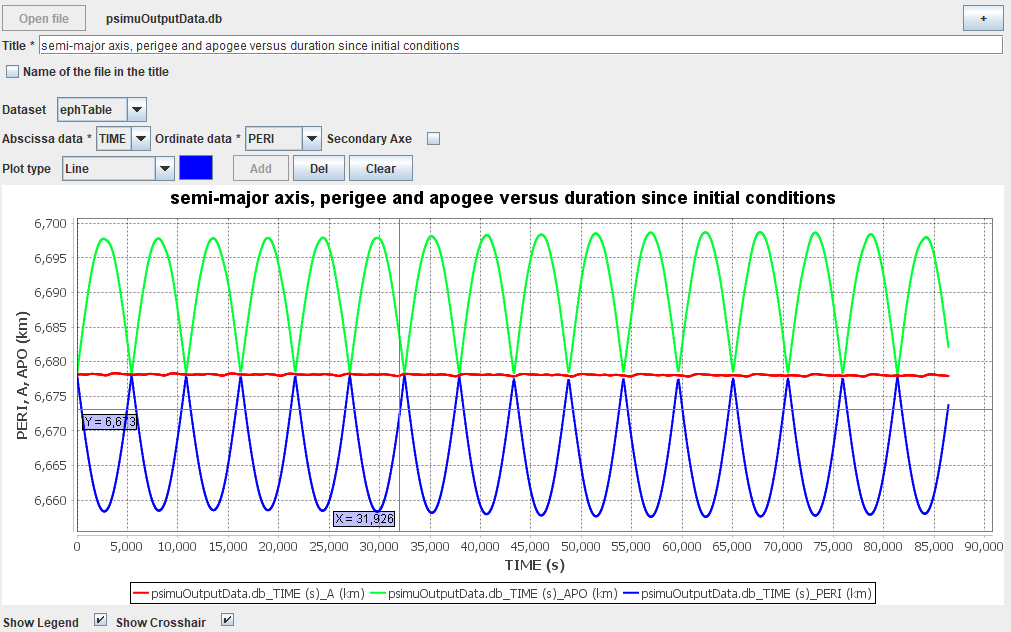
But, in the same tab, the user will have access to a graphical display (only available after propagation has occurred).
| Acronym | Description | Unit |
| DATE | Date (TAI) | - |
| TIME | Duration since initial conditions | sec |
| TMASS | Total mass | kg |
| PMASS | Propellant mass | kg |
| XIN | Inertial x coordinates | m |
| YIN | Inertial y coordinates | m |
| ZIN | Inertial z coordinates | m |
| VXIN | Velocity in inertial x coordinates | m/s |
| VYIN | Velocity in inertial y coordinates | m/s |
| VZIN | Velocity in inertial z coordinates | m/s |
| POSIN | Position norm in inertial frame | m |
| VIN | Velocity norm in inertial frame | m/s |
| XREL | X component of the relative position in rotating frame | m/s |
| YREL | Y component of the relative position in rotating frame | m/s |
| ZREL | Z component of the relative position in rotating frame | m/s |
| VXREL | X component of the relative velocity in rotating frame | m/s |
| VYREL | Y component of the relative velocity in rotating frame | m/s |
| VZREL | Z component of the relative velocity in rotating frame | m/s |
| VREL | Relative velocity in rotating frame | m/s |
| A | Semi-major axis | km |
| E | Eccentricity | - |
| I | Inclination | deg |
| AOP | Aargument of perigee | deg |
| RAAN | Right ascension of the ascending node | deg |
| TA | True anomaly | deg |
| MA | Mean anomaly | deg |
| EA | Eccentric anomaly | deg |
| EX | First component of the eccentricity vector | - |
| EY | Second component of the eccentricity vector | - |
| HX | First component of the inclination vector | - |
| HY | Second component of the inclination vector | - |